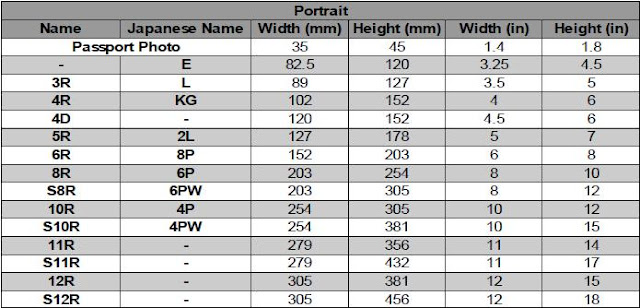
Nik Collection by Google
Shared publicly - 25 Mar 2016
Today we’re making the Nik Collection available to everyone, for free.
Photo enthusiasts all over the world use the Nik Collection to get the best out of their images every day. As we continue to focus our long-term investments in building incredible photo editing tools for mobile, including Google Photos and Snapseed, we’ve decided to make the Nik Collection desktop suite available for free, so that now anyone can use it.
The Nik Collection is comprised of seven desktop plug-ins that provide a powerful range of photo editing capabilities -- from filter applications that improve color correction, to retouching and creative effects, to image sharpening that brings out all the hidden details, to the ability to make adjustments to the color and tonality of images.
Starting March 24, 2016, the latest Nik Collection will be freely available to download: Analog Efex Pro, Color Efex Pro, Silver Efex Pro, Viveza, HDR Efex Pro, Sharpener Pro and Dfine. If you purchased the Nik Collection in 2016, you will receive a full refund, which we’ll automatically issue back to you in the coming days.
We’re excited to bring the powerful photo editing tools once only used by professionals to even more people now.
Photo enthusiasts all over the world use the Nik Collection to get the best out of their images every day. As we continue to focus our long-term investments in building incredible photo editing tools for mobile, including Google Photos and Snapseed, we’ve decided to make the Nik Collection desktop suite available for free, so that now anyone can use it.
The Nik Collection is comprised of seven desktop plug-ins that provide a powerful range of photo editing capabilities -- from filter applications that improve color correction, to retouching and creative effects, to image sharpening that brings out all the hidden details, to the ability to make adjustments to the color and tonality of images.
Starting March 24, 2016, the latest Nik Collection will be freely available to download: Analog Efex Pro, Color Efex Pro, Silver Efex Pro, Viveza, HDR Efex Pro, Sharpener Pro and Dfine. If you purchased the Nik Collection in 2016, you will receive a full refund, which we’ll automatically issue back to you in the coming days.
We’re excited to bring the powerful photo editing tools once only used by professionals to even more people now.